Blender is for Video Editors
Blender comes with a built-in video sequence editor allows you to perform basic actions like video cuts and splicing, as well as more complex tasks like video masking or color grading.
- Live preview, luma waveform, chroma vectorscope and histogram displays.
- Audio mixing, syncing, scrubbing and waveform visualization.
- Up to 32 slots for adding video, images, audio, scenes, masks and effects.
- Speed control, adjustment layers, transitions, keyframes, filters and more!
Explore the expansive world of Blender, a powerhouse for 3D modeling, animation, and video editing. From beginner tutorials to advanced animation techniques, our review covers everything you need to know about this versatile, free software. Whether you’re creating stunning 3D art or editing video projects, Blender offers all the tools required for high-quality content creation.
>> You may be interested: Best Video Editing Software for PC

Blender: The Ultimate 3D Creation Suite with Video Editing Capabilities
- Blender stands as a titan in the digital content creation world, offering an unparalleled suite of tools for 3D modeling, animation, and video editing—all within a single, open-source platform. Originating as an in-house tool in 1995, Blender has evolved dramatically, thanks to its community-driven development, into a comprehensive solution that caters to professional artists and hobbyists alike. This evolution reflects Blender’s commitment to accessibility and innovation, securing its place as a preferred choice for creators seeking a robust, no-cost alternative in the 3D and video editing domains.
Section 1: Embarking on Your Blender Journey
Embarking on a journey with Blender opens up a world of creative possibilities in both 3D creation and video editing. This section introduces new users to the Blender interface, emphasizes its dual capabilities, outlines the system requirements, and guides through the downloading and installation process.
Navigating Blender’s Interface:
Blender’s interface might seem daunting at first glance due to its comprehensive suite of tools and a non-linear editing approach. The interface is highly customizable, and designed to accommodate a wide range of tasks from 3D modeling and animation to video editing within the Video Sequence Editor (VSE). Familiarizing yourself with the layout – including the 3D viewport, timeline, and properties panel – is the first step to harnessing Blender’s full potential.
Dual Capabilities in 3D and Video Editing:
Blender uniquely integrates robust 3D modeling and animation tools with video editing capabilities, making it a versatile choice for creators who wish to delve into both worlds. While primarily celebrated for its 3D features, Blender’s Video Sequence Editor offers a powerful, track-based video editing environment, suitable for tasks ranging from simple cuts to complex compositions with effects and color grading.
System Requirements for Running Blender Efficiently:
To run Blender smoothly, your system should meet the following minimum requirements:
- Operating System: Windows 8.1, macOS 10.13, Linux
- Processor: 64-bit dual-core 2Ghz CPU with SSE4.2 support
- Memory: 4 GB RAM
Graphics: 1 GB RAM, OpenGL 4.3
- Higher specifications are recommended for more demanding projects, particularly those involving complex simulations or high-resolution textures and renders.
Guide to Downloading and Installing Blender:
Getting Blender up and running is straightforward:
- 1. Visit Blender’s Official Website: Go to blender.org, where you’ll find the latest version of Blender available for download.
- 2. Choose Your Version: Select the version compatible with your operating system. Blender provides versions for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- 3. Download: Click the download link. The website might automatically detect your OS and suggest the appropriate version.
- 4. Install: Once downloaded, run the installer and follow the on-screen instructions to install Blender on your computer.
- 5. Launch Blender: After installation, open Blender to start exploring its features. Consider customizing the interface to suit your workflow.
Section 2: Mastering 3D Modeling and Animation with Blender
Blender’s comprehensive suite of 3D modeling and animation tools caters to creators at all levels, from beginners crafting their first model to professionals developing complex animations. This section explores the core aspects of Blender’s 3D capabilities, providing insights and steps to embark on 3D modeling and animation.
Exploring Blender’s 3D Modeling Tools and Features:
Blender offers an extensive array of 3D modeling tools that allow for the creation of everything from simple shapes to intricate models. Key features include:
- Mesh Modeling: The backbone of 3D modeling in Blender, mesh tools let you manipulate vertices, edges, and faces to shape your objects.
- Sculpting: For more organic shapes, Blender’s sculpting tools offer a more hands-on approach, mimicking the process of sculpting clay.
- Modifiers: Non-destructive tools that automate tasks like smoothing, bending, or adding complexity to your models, speeding up the workflow.
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Your First 3D Model:
- Open Blender and Create a New Project: Start with a blank scene.
- Understand the 3D Viewport: Navigate the viewport to get a good view of your workspace.
- Add a Mesh: Use the “Add” menu to insert a basic mesh, like a cube, as the starting point for your model.
- Edit Your Mesh: Enter Edit Mode (Tab key) and start shaping your object using the vertices, edges, and faces.
- Experiment with Modifiers: In the Properties Panel, explore modifiers like Subdivision Surface to smooth out your model.
- Apply Materials: Switch to the Shading workspace to add colors or textures, giving life to your model.
Overview of Animation Tools:
Blender’s animation tools bring models to life, ranging from simple keyframe animations to complex character rigs:
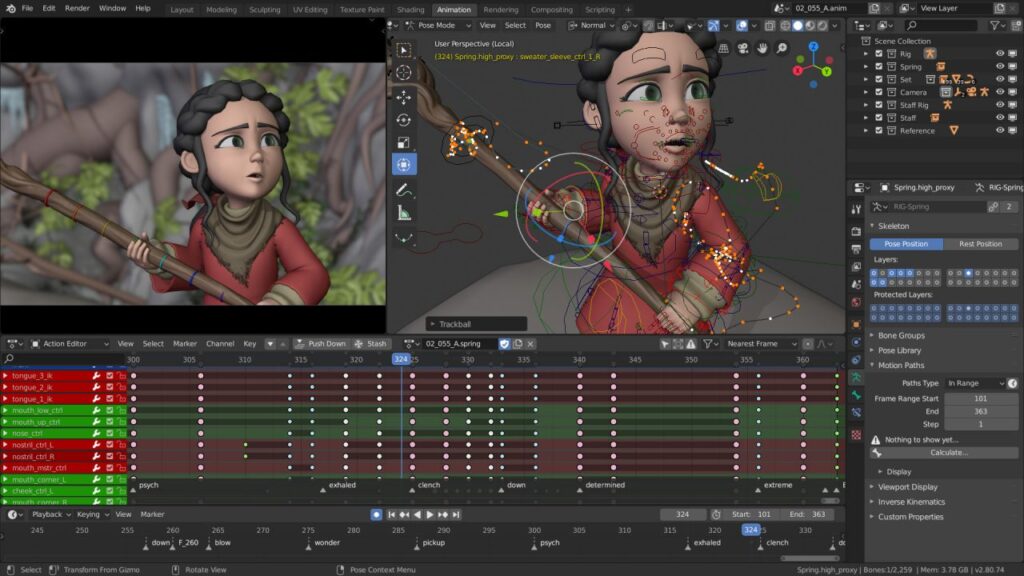
- Keyframe Animation: Easily animate movement, rotation, and scale by inserting keyframes at different points in your timeline.
- Armatures and Rigging: For character animation, Blender allows you to create a skeletal structure (armature) and define how your model moves in relation to this rig.
- Shape Keys: Useful for facial expressions or morphing objects, shape keys let you transition between different states of a model.
Tips for Rendering and Exporting Your 3D Projects:
Rendering transforms your 3D scene into a final image or animation. Here are some tips to optimize this process:
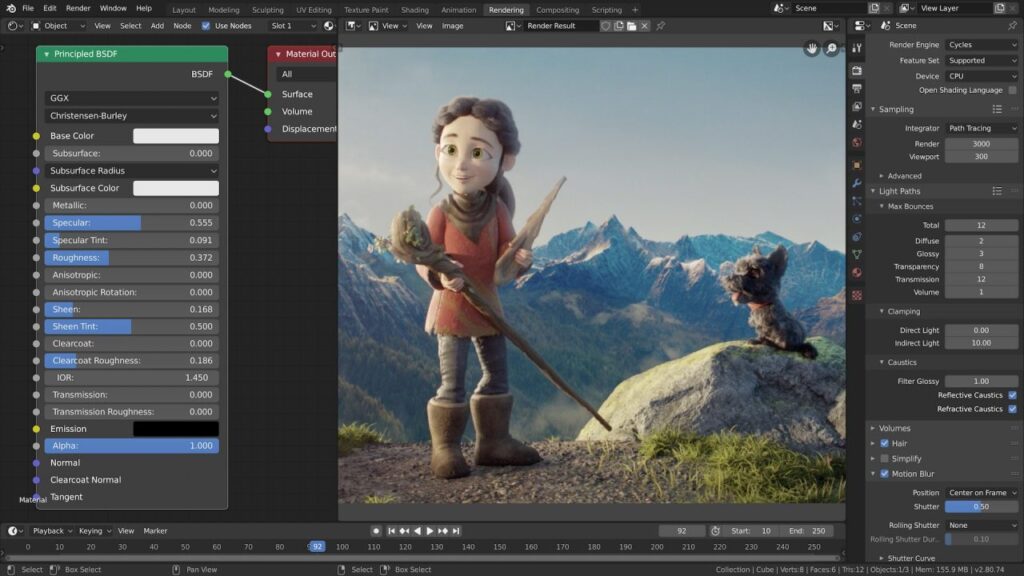
- Choose Your Renderer: Blender includes different rendering engines like Eevee (real-time) and Cycles (ray-traced). Pick one based on your needs and system capabilities.
- Optimize Settings: Adjust rendering settings such as resolution, sampling, and lighting to balance quality with render time.
- Use Camera Views: Place cameras strategically in your scene to capture the desired angles and compositions.
- Exporting: Blender supports exporting to various formats. For animations, choose a video format under the Output Properties; for models, use the File > Export options to select a format compatible with your needs or other software.
Section 3: Unlocking Blender’s Video Editing Power
While Blender is renowned for its 3D modeling and animation capabilities, its Video Sequence Editor (VSE) offers a robust platform for video editing, blending basic and advanced functions into a comprehensive toolkit. This section delves into the VSE, guiding users through its video editing capabilities and post-production features.
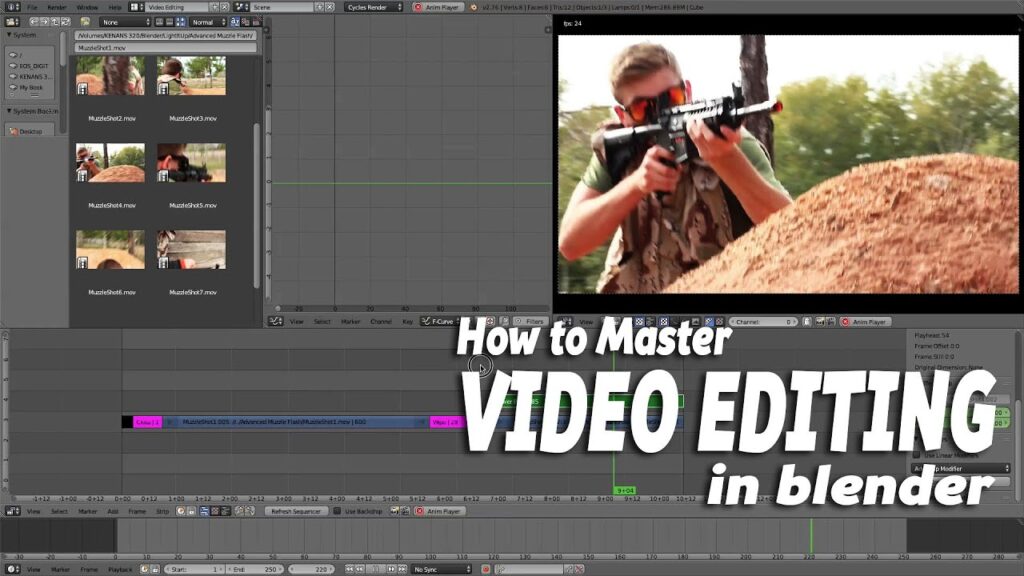
Introduction to Blender’s Video Sequence Editor (VSE):
Blender’s VSE is a non-linear video editor embedded within the same environment, allowing users to edit video footage, combine video clips with 3D scenes, and apply effects and transitions. It supports a wide range of video and audio formats, enabling seamless integration of various media types into your projects.
Basic Video Editing Functions:
- Cutting and Trimming: The VSE allows for easy cutting and trimming of video clips. Simply select a clip in the timeline, use the soft or hard cut commands to slice it at the desired point, and remove or adjust the segments to fit your narrative flow.
- Sequencing: Arrange your clips on the timeline, dragging and dropping them into position. Blender’s VSE supports multiple channels, offering the flexibility to layer videos and audio tracks for complex compositions.
Advanced Video Editing Features:
- Effects: Blender includes several built-in effects, like color correction, blurs, and glows, which can be added to your video clips directly in the VSE. These effects can enhance the visual appeal of your footage or correct color imbalances.
- Transitions: Create smooth transitions between clips using Blender’s array of transition options, such as crossfades, wipes, and slides, adding a professional polish to your edits.
- Color Grading: The VSE’s color grading tools enable you to adjust the mood and tone of your footage, with controls for color balance, curves, and levels, ensuring your final product matches your artistic vision.
Utilizing Blender for Post-Production Tasks:
- Compositing: Blender’s powerful compositing features can be accessed within the VSE, allowing you to combine video footage with rendered 3D elements, create special effects, or apply green screen techniques for background replacement.
- Motion Tracking: For more advanced post-production tasks, Blender offers a motion-tracking toolset. This can be particularly useful for integrating 3D elements into live-action footage, ensuring they move convincingly with the camera.
Section 4: Expanding Creativity with Blender’s Unique Features and Extensions
Blender is not just another 3D software; it’s a comprehensive creative suite that stands out with unique features and a vast ecosystem of extensions and third-party content. This section explores the standout features of Blender, such as the Grease Pencil, sculpting capabilities, and simulations, along with how add-ons and third-party content can significantly enhance Blender’s functionality and your creative projects.
Highlighting Blender’s Standout Features:
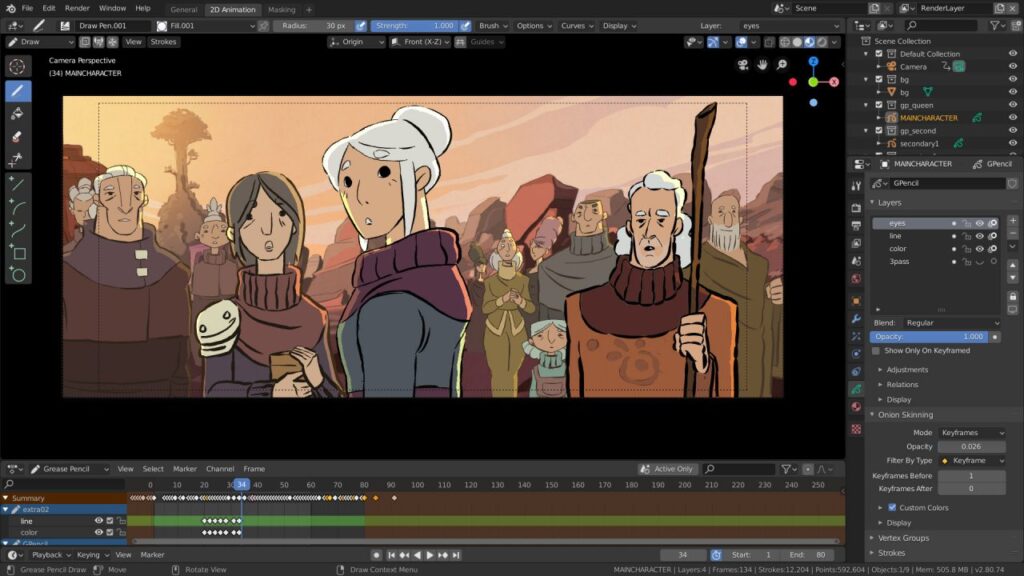
- Grease Pencil: Revolutionizing the bridge between 2D and 3D, Blender’s Grease Pencil tool allows artists to draw directly in the 3D space, creating 2D animations and storyboards within a 3D environment. This unique feature supports traditional frame-by-frame animation techniques, offering a new realm of possibilities for 2D animators and concept artists.
- Sculpting: Blender’s sculpting tools are on par with dedicated sculpting software, offering a high level of detail and flexibility. Dynamic topology, multiresolution sculpting, and a variety of brushes allow for intricate model creation, making Blender a favorite among character artists and digital sculptors.
- Simulations: Blender’s physics engine supports a wide range of simulations, including cloth, fluid, smoke, hair, and particle systems. These simulations can add realism to scenes, create dynamic effects, or simulate natural phenomena, providing a powerful toolset for visual effects artists and animators.
Overview of Add-Ons and Extensions to Enhance Blender’s Functionality:
Blender’s functionality can be further expanded with add-ons and extensions, many of which are developed by the community:
- Add-Ons for Productivity: From workflow enhancements to specialized modeling tools, add-ons can streamline your creative process, saving time and effort.
- Extensions for Rendering: Enhance your rendering capabilities with extensions that introduce new render engines or optimize existing ones, improving both quality and speed.
- Content Libraries: Access libraries of materials, textures, and models through add-ons, enriching your projects without the need to create every asset from scratch.
Integrating Third-Party Content and Effects into Blender Projects:
Blender’s open architecture makes it particularly adept at incorporating third-party content and effects:
- Importing Models and Assets: Blender supports various file formats, allowing for easy import of models, textures, and animations from other software or online marketplaces.
- Using Third-Party Shaders and Effects: Expand Blender’s visual effects capabilities with custom shaders and effects, available through community forums or commercial providers.
- Collaborating Across Software: With support for industry-standard file formats like Alembic and USD, Blender facilitates seamless collaboration in multi-software pipelines, ensuring that it plays well in diverse creative environments.
Section 5: Navigating Blender’s Learning Curve with Resources and Community Support
Blender, with its comprehensive capabilities, presents a steep learning curve. Fortunately, an extensive array of tutorials, a supportive community, and a wealth of third-party courses and guides are available to flatten this curve significantly. This section outlines the best practices for accessing Blender tutorials suitable for all skill levels, engaging with Blender’s online community, and finding third-party educational resources to master Blender.
Accessing Blender Tutorials for Beginners and Advanced Users:
- Blender.org: The official Blender website is a treasure trove of learning resources, including tutorials that cover everything from the basics to more advanced topics.
- Blender Guru: For many users, Blender Guru’s tutorials, especially the famous “Donut” series, serve as an ideal starting point for beginners, offering step-by-step guidance through fundamental concepts.
- CG Cookie: This platform offers a wide range of Blender tutorials and courses, catering to both new users and seasoned professionals looking for advanced techniques.
Overview of Blender’s Vast Online Community and Support Forums:
- Blender Artists Community: One of the largest forums dedicated to Blender, offering a space for users to share work, ask questions, and receive feedback from fellow Blender enthusiasts.
- Blender Network: Connecting Blender professionals and enthusiasts worldwide, the Blender Network is a great place to find collaborators, job opportunities, and professional services.
- r/blender: The Blender subreddit is an active community where users share their projects, tutorials, and tips, fostering a supportive environment for learning and improvement.
Recommended Third-Party Courses and Guides for Mastering Blender:
- Udemy and Coursera: Both platforms feature comprehensive Blender courses that cover a wide range of topics, from 3D modeling and animation to VFX and game development, suitable for different skill levels.
- YouTube Channels: Besides Blender Guru, channels like CG Geek, Ducky 3D, and Gleb Alexandrov offer in-depth tutorials and projects to help users harness Blender’s full potential.
- Books and E-books: For those who prefer written guides, books like “Blender For Dummies” and “The Complete Guide to Blender Graphics” are excellent resources that cover a broad spectrum of Blender’s functionality.
With the right resources at your disposal, learning Blender becomes a manageable and rewarding endeavor. The Blender community is known for its willingness to help newcomers, so don’t hesitate to seek advice and feedback on your learning journey. Whether you’re starting with your first 3D model or diving into complex animations, the wealth of tutorials, community support, and third-party guides will ensure you have all the knowledge and assistance you need to succeed with Blender.
Section 6: Voices from the Blender Community: User Experience and Success Stories
Blender’s impact on the world of digital creation is best illustrated through the voices of its vast user base, from individuals embarking on their first 3D modeling journey to professionals utilizing it in high-stakes environments. This section compiles testimonials, professional feedback, and real-world success stories, showcasing the transformative power and versatility of Blender.
Compiling User Testimonials and Professional Feedback:
- From Novices to Experts: Blender’s learning curve is often mentioned in user testimonials, with beginners expressing initial challenges that give way to satisfaction as they unlock new capabilities. Experienced users, including professionals in the 3D industry, often highlight Blender’s robust feature set and flexibility, comparing it favorably to industry-standard software.
- A Tool for Creativity: Many users testify to Blender’s role in bringing their imaginative visions to life, whether through animations, simulations, or detailed 3D models. The integrated workflow—combining modeling, animation, and video editing—allows for a seamless creative process.
- Open Source as a Strength: The open-source nature of Blender is frequently praised for fostering a collaborative environment where users can contribute to its development, share assets and plugins, and access the software for free, making it accessible to everyone.
Real-world Success Stories and Project Highlights:
- Indie Film Projects: Independent filmmakers share how Blender enabled them to produce visually stunning animations and VFX on limited budgets, often highlighting specific features like the Grease Pencil for storyboarding or Blender’s VSE for post-production.
- Game Development: Game developers recount using Blender for creating detailed game assets and environments, praising its integration with major game engines and the ability to prototype rapidly.
- Academic and Scientific Visualization: Educators and researchers utilize Blender for creating educational content and visualizing complex scientific data, demonstrating the software’s versatility beyond entertainment and art.
- Commercial Successes: Companies in the advertising and architectural visualization industries showcase projects where Blender was crucial in developing high-quality visuals and animations, underscoring its capability to meet professional demands.
These stories and testimonials from the Blender community not only underscore the software’s technical prowess but also its role in democratizing 3D creation. By offering a powerful, free tool, Blender empowers individuals and organizations worldwide to explore their creativity, innovate, and share their stories through stunning visuals and animations. The collective success of the Blender community is a testament to the software’s impact, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in digital art and content creation.
Section 7: Blender in the Competitive Landscape
As Blender continues to evolve, it becomes increasingly important to understand how it stands against other stalwarts in the 3D and video editing arena. This comparison aims to highlight Blender’s position relative to industry standards like Maya, Cinema 4D, and Adobe Premiere Pro, offering insights into its suitability for different user groups, from hobbyists to professional studios.
Side-by-Side Comparison with Industry Standards:
- Blender vs. Maya:
|
Primary Rating:
4.7
|
Primary Rating:
4.5
|
|
Free
|
$1,875/year for 1 user
|
|
User Base:
Blender appeals to a broader user base, from hobbyists to professionals, due to its no-cost model.
|
User Base:
Maya is widely used in the film and gaming industries for its advanced animation and modeling tools
|
|
Features:
Blender closes this gap with continuous updates and a comprehensive feature set, including the Grease Pencil for 2D/3D hybrid animations.
|
Features:
While both offer robust toolsets for 3D modeling, animation, and rendering, Maya has traditionally been preferred for character animation in high-budget film production.
|
|
Pricing Model:
Maya operates on a subscription model with a significant annual cost, making Blender an attractive alternative for individuals and small studios looking to minimize expenses.
|
Pricing Model:
Maya operates on a subscription model with a significant annual cost, making Blender an attractive alternative for individuals and small studios looking to minimize expenses.
|
- Blender vs. Cinema 4D:
-
-
- Ease of Use: Cinema 4D is praised for its user-friendly interface and ease of learning, making it popular among graphic designers and motion graphics artists. Blender, with recent updates, has improved its interface for a more intuitive experience, although it has a steeper learning curve.
- Motion Graphics: Cinema 4D remains a go-to for motion graphics due to its powerful MoGraph module. Blender competes with its own set of animation tools and a growing library of extensions for motion graphics.
- Community and Resources: Both have strong communities; however, Blender’s open-source nature and free access result in a wide array of tutorials, forums, and user-generated content.
-
- Blender vs. Adobe Premiere Pro (For Video Editing):
|
Primary Rating:
4.7
|
Primary Rating:
4.5
|
|
Free
|
Free
|
|
Primary Use Case:
Blender’s Video Sequence Editor provides a capable alternative for video editing within a 3D creation suite, suitable for projects that require integration of 3D elements.
|
Primary Use Case:
Adobe Premiere Pro is a dedicated video editing software, part of the Adobe Creative Cloud suite, making it ideal for video editors and content creators focused on post-production.
|
|
Integration:
Blender stands out for projects that benefit from closely integrated 3D modeling, animation, and video editing within the same application.
|
Integration:
Premiere Pro offers seamless integration with other Adobe applications, enhancing its video editing capabilities
|
|
Pricing Model:
Blender remains free, offering a viable option for those on a tight budget or needing a comprehensive 3D and video editing tool without additional cost.
|
Pricing Model:
Adobe Premiere Pro requires a monthly subscription, part of the Creative Cloud suite.
|
Evaluating Blender for Various Creator Needs:
- Hobbyists and Indie Creators: Blender is an excellent choice for those starting out or working on independent projects. Its zero-cost entry point, combined with a vast array of features, makes it accessible and powerful for creating high-quality 3D art and animations.
- Professional Studios: While high-end studios might prefer specialized software like Maya for specific tasks (e.g., character animation for film), Blender is increasingly adopted for its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and quality outputs. Its suitability for professional work continues to grow, evidenced by its use in commercial projects and indie films.
Blender’s comprehensive toolset, community support, and cost-free model present a compelling case for various user groups. Whether for 3D modeling, animation, or video editing, Blender stands as a formidable competitor in the digital content creation space, offering an all-in-one solution that meets a wide range of creative needs.
Section 8: Embracing the Open-Source Ethos: Updates, Pricing, and Contributions to Blender
Blender’s journey as a premier open-source 3D creation suite is a testament to the power of community and the open-source model. This section delves into how Blender manages to stay ahead with regular updates, remains accessible at no cost, and how the broader community can contribute to its ongoing development.
Blender’s Open-Source Model and Update Cycle:
Blender thrives under an open-source license, meaning its source code is freely available for anyone to study, modify, and distribute. This approach fosters a transparent development process, encouraging contributions from developers worldwide. The result is a robust, constantly evolving software that reflects the needs and innovations of a diverse user base.
- Regular Updates: Blender’s development cycle includes frequent updates, ranging from minor bug fixes to major releases that introduce new features and improvements. These updates are informed by community feedback and contributions, ensuring Blender remains relevant and on the cutting edge of 3D technology.
How Blender Remains Free:
Blender remains free to download and use for any purpose, commercial or non-commercial, thanks to its open-source licensing. This decision is rooted in the Blender Foundation’s mission to provide a complete, free, and open-source 3D creation pipeline.
- Funding: The Blender Foundation, a non-profit organization responsible for Blender’s development, funds its operations through donations, grants, and corporate sponsorships. The Blender Development Fund, supported by donations from users and industry patrons, plays a crucial role in financing the project’s ongoing development and ensuring Blender remains free for all.
Ways Users Can Contribute to Blender’s Development:
Contributing to Blender goes beyond coding. Users can support Blender’s development and community in several meaningful ways:
- Development Contributions: If you have programming skills, you can contribute to Blender’s codebase, submit bug reports, or develop new features and add-ons.
- Financial Support: Joining the Blender Development Fund through monthly donations supports the core development team and project initiatives. Every contribution, no matter the size, makes a difference.
- Content Creation: Sharing tutorials, creating educational content, or contributing to the Blender community with templates and resources helps new users and enriches the ecosystem.
- Spreading the Word: Advocating for Blender in your professional networks, social media, or educational institutions raises awareness and introduces more people to the software, growing the community and potential development support.
Blender’s story is one of collaboration, innovation, and community. Its open-source model not only ensures the software remains free and accessible but also invites a global community of users and developers to shape its future. Whether through code, contributions, or creativity, everyone has the opportunity to be a part of Blender’s ongoing journey, reinforcing its position as a leading tool in digital content creation.
Section 9: Beginning Your Creative Journey with Blender
As we conclude our exploration of Blender, it’s clear that this open-source powerhouse stands as a beacon for digital artists, animators, and video editors worldwide. Offering an unparalleled array of tools for 3D modeling, animation, rendering, and video editing — all under a no-cost license — Blender empowers creatives to bring their visions to life without financial barriers. Here’s a brief recap and words of encouragement for those about to start their Blender journey.
Blender’s Multifaceted Capabilities:
Blender’s versatility as a 3D creation suite is unmatched, providing professionals and hobbyists alike with:
- Advanced 3D modeling and sculpting tools for creating detailed characters, environments, and objects.
- Powerful animation features for bringing models to life with fluid movements.
- A comprehensive set of rendering options, including the real-time Eevee and the physically accurate Cycles.
- Integrated video editing capabilities within the Video Sequence Editor, allowing for seamless post-production of animation and film projects.
- An extensive library of extensions, add-ons, and community-generated content to expand its functionality.
Diving Into Blender with Confidence:
To new users embarking on their Blender journey, remember that the path to mastering Blender is a journey of continuous learning and experimentation. The robust community and wealth of learning resources available make it easier than ever to start:
- Utilize the multitude of tutorials available online, from beginner guides to advanced project walkthroughs.
- Engage with the Blender community through forums, social media, and user groups to share experiences, seek advice, and find inspiration.
- Embrace experimentation within Blender to discover your unique creative workflow and unlock the full potential of its features.
Appendix: FAQs
- How do I download Blender?
- Visit blender.org and navigate to the download section to choose the version that matches your operating system.
- What are the system requirements for Blender?
- While Blender can run on a wide range of hardware, check the official Blender website for the latest recommendations to ensure optimal performance.
- Where can I find Blender tutorials?
- The Blender website, YouTube, and online learning platforms like Udemy and CG Cookie offer extensive tutorials for all skill levels.
- How can I resolve common issues in Blender?
- Consult the official Blender manual and forums for troubleshooting tips. Many user issues can be resolved by updating graphics drivers, adjusting settings, or seeking advice from the community.
- How can I contribute to Blender?
- Contributions can be made through code submissions, joining the Blender Development Fund, or creating and sharing resources with the community.
To Conclude
Starting your journey with Blender opens up a world of creative possibilities. With dedication and the support of the Blender community, you’re well on your way to creating incredible 3D art and animations. Embrace the challenge, and let Blender be your tool of choice for expressing your creativity and bringing your digital dreams to reality.
Maybe you should look into other video editor apps